Introduction
A radio receiver (RX) is a crucial component in an FPV drone, responsible for receiving signals from the pilot’s radio transmitter and relaying them to the flight controller. Choosing the right receiver impacts range, latency, and overall flight performance. This guide covers different types of radio receivers, focusing on ExpressLRS (ELRS) and other popular protocols used in FPV drones.
What is a Radio Receiver?
A radio receiver is an electronic device that decodes signals sent by the radio transmitter and converts them into commands for the flight controller. These receivers operate on different protocols, each offering unique features like low latency and long-range capabilities.

Types of Radio Receivers
- ExpressLRS (ELRS)
- A modern, open-source radio protocol known for ultra-low latency and long-range capabilities.
- Operates on 2.4GHz and 900MHz bands.
- Offers flexible output power from 25mW to 1000mW, depending on hardware.
- Used in both racing and long-range FPV setups.
- FrSky Receivers
- Common in FPV drones and RC planes.
- Supports ACCST and ACCESS protocols.
- Includes models like FrSky R-XSR, XM+, and Archer receivers.
- Works well with FrSky transmitters such as Taranis X9D, QX7, and X-Lite.
- TBS Crossfire (CRSF) Receivers
- Designed for long-range FPV flights, operating on 868MHz (EU) and 915MHz (US).
- Offers reliable signal penetration through obstacles.
- Ideal for freestyle and cinematic drone pilots.
- Ghost by ImmersionRC
- Focused on ultra-low latency and high refresh rates.
- Suitable for high-speed drone racing.
- Uses 2.4GHz frequency band with minimal interference.
- Spektrum Receivers (DSM2/DSMX)
- Used primarily in traditional RC aircraft.
- DSMX offers better frequency-hopping and improved interference resistance.
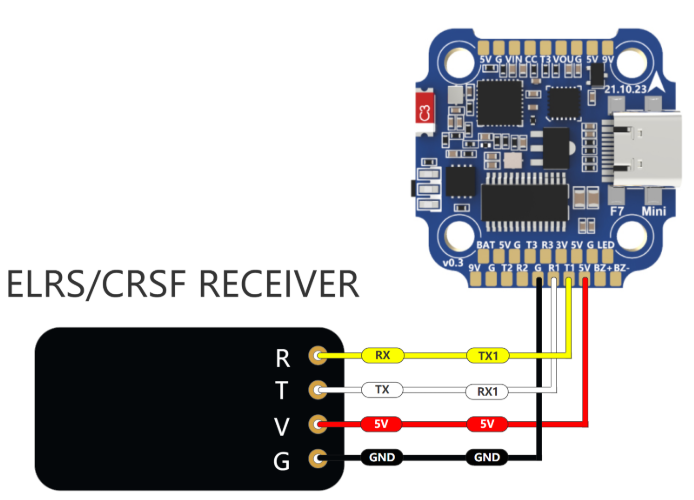
Circuit Diagram: Connecting a Receiver to a Flight Controller
A radio receiver typically connects to the flight controller via the UART (Serial) or SBUS/CRSF ports. Below is a basic wiring diagram:
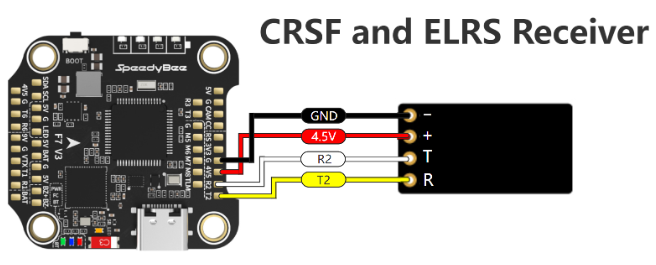
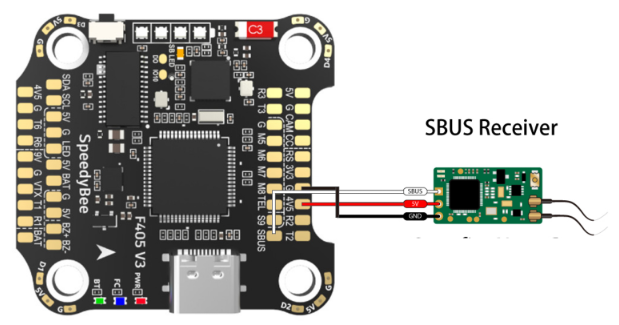
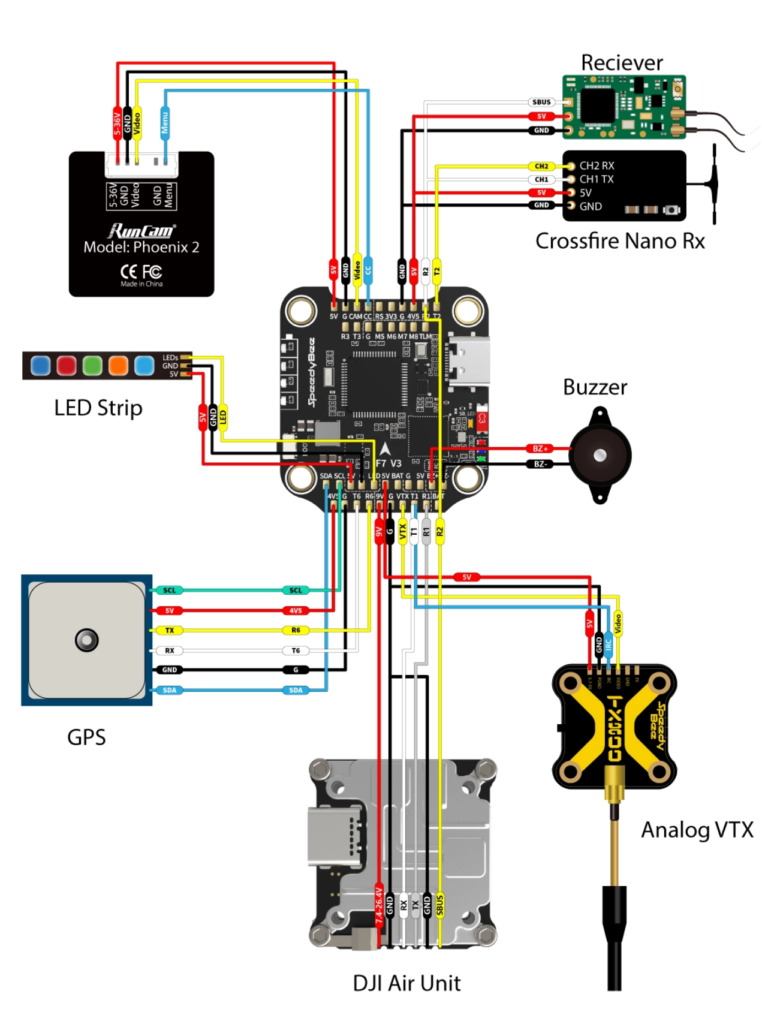
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Radio Receiver
- Compatibility: Ensure it matches your transmitter’s protocol.
- Latency: Lower latency improves control response.
- Range: Long-range pilots should choose ELRS, Crossfire, or Ghost.
- Antenna Type: Diversity antennas improve signal stability.
BetaFlight SetUp Below
Check if the ‘Serial Rx’ is enabled for the receiver
For example, if your receiver is connected to UART 2, then you should enable ‘Serial Rx’ on UART 2.
Note: You can only enable one item in the whole UART row because one UART can only connect one peripheral. For example, if you set UART 2 as Serial Rx, you can’t enable configuration/MSP, Telemetry Output, Sensor Input, or Peripherals.
Set the correct receiver mode and provider.
You should do this due to your receiver’s manual:
- TBS Crossfire – CRSF
- ExpressLRS – CRSF
- Spektrum DSM2 – SPEKTRUM1024/SRXL2
- Spektrum DSMX – SPEKTRUM2048/SRXL2
- FrSky RX – SBUS
- Futaba RX – SBUS
- FlySky RX – IBUSTurnigy RX – IBUS
For example, if your receiver is TBS Crossfire or ELRS, please choose ‘CSRF’
Choose ‘Serial(via UART)’ and ‘SBUS’ for Frsky receivers:
Choose PPM or IBUS for Flysky receivers:
Betaflight 4.4.0 Cloud-Build SBUS ,CRSF GHST)
Check if your transmitter can be detected in the Betaflight configurator.
Connect your flight controller to the Betaflight configurator > Receiver tab, move the sticks or toggle the switches to see if the Betaflight UI can show the input correspondingly.
NOTE: for some receivers, you must keep them at least 0.5 meters far away from the transmitter to prevent the connection from being disconnected automatically.
Conclusion
Selecting the right radio receiver is crucial for achieving a smooth FPV experience. Whether you need low latency for racing or long-range performance for freestyle, understanding different receiver types helps optimize your drone’s communication system. ExpressLRS is currently the leading choice for most pilots due to its balance of range, speed, and open-source flexibility.
Stay tuned for more FPV drone insights!





GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings